Topic 1: Germany in the World

Lesson 4: What is the landscape of Germany?
Lesson Objective
- The student will describe the climate and topography of Germany.
- The student will explain the relationship between climate and location.
Materials and Resources
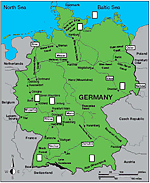 Transparency 1 - “Geography of Germany” |
 Transparency 2 - “Beautiful Places in Germany” |
- Worksheet 6 - “Geography of Germany”
- Teacher Resource 4 - “Beautiful Places in Germany”
- Worksheet 7 - “The German Landscape”
- Worksheet 8 - “The Geographic Regions of Germany”
Strategies
Germany’s geography rises from the flat lowlands in the north to the towering Alps Mountains in the south. Numerous rivers wind through the countryside. Germany’s geography is varied; as a rule, the further south you go, the more mountainous is the landscape. The northern part, where Bremen and Hamburg are located, is very flat. Because this area is on the sea, there is a lot of shipping. The ground is often wet and marshy. In the central part of Germany there is more heavy industry such as coal mining, chemicals and steel production. The land is fairly flat with a few hills, and is used for farming. All sorts of food are grown: grain, fruit, potatoes, vegetables, and corn and hay for farm animals. Along the Rhine River, grapes are grown to produce wine. In the southwest corner of Germany is the Black Forest, a large hilly area covered with tall pine trees, occasionally broken up by small villages.
On the border of Germany with Switzerland and Austria, there is a series of lakes created by glaciers. This border is also where the Alps begin.
To help students identify various types of landforms, distribute copies of Worksheet 6, “Geography of Germany” to students. Next, show the transparencies of Teacher Resource 4, “Beautiful Places in Germany.” For each picture, read the clue from the chart below and ask students to write the corresponding number of the picture in the box on the map on the worksheet.
| Place | Clue | |
| Baltic Sea | The white beach, the white rocks and the mild climate in summer have been a fascinating attraction for Germans for many centuries. | |
| Rhine River | One of the most famous areas on the romantic Rhine River is the area almost opposite to Bonn: the mountain range called Seven Mountains with the legendary ruin of an old fortress “Dragon Rock” (Drachenfels), where Siegfried, the main hero in the Nibelungen Saga is said to have had his battle with a dragon. | |
| Elbe River and Dresden | Dresden is called “Florence on the Elbe River” with its splendid castles, museums, galleries, churches and theater buildings. | |
| Amorbach (Odenwald) | Even nowadays, one of the largest forests is still known for its beautiful leaved trees and its deer. Hunting in the Odenwald was legendary in the Middle Ages. Siegfried is said to having been killed by his guard in this forest while hunting. There are lots of small towns like Amorbach, totally surrounded by dense forests. | |
| Lübeck | With its channels and its gothic brick stone buildings, Lübeck, the “mother of the strong Hansa”, the trade association of free towns, is a model for northern culturally rich towns. | |
| Limburg | There are many beautiful small old towns on the Lahn River, most in halftimber style. As salt was as precious as gold in the Middle Ages because of its conservation function for meat and fish, towns on the “Salt street” from the north to the south made a good profit from this trade. | |
| Black Forest | The Black Forest in the southern corner of Germany, between France and Switzerland is originally a strong fir forest region famous for its fairy tales and the handicraft tradition of cuckoo clock works. Nowadays, it attracts tourists from all over the world to its spas. | |
| Chiemsee, Fraueninsel | With the background of the Alps the Chiemsee with its two isles, fairy tale like castles and monasteries and a special mild climate is a center of tourism. |
Have students demonstrate their understanding of the regions of the landscape of Germany by cutting the photographs from Worksheet 7, “The German Landscape” and gluing them at the correct location on Worksheet 8, “The Geographic Regions of Germany.”

 Printable PDF
Printable PDF